This page was intended to be an update to page 6 of these module notes. ELMS however diabled all the features on the linked pages. The technical help people do far have been unable to provide a solution. While some features have been disabled, there is still some important text about each enzyme in the pathways as well as a rationale for how the pathways (glycolysis and gluconeogeneis) fit together. I apologize for the issue but I do not know how to solve it. There were some neat (if I don't say so myself) learning tools on the linked pages. Please do notice, however, the key differences between the two pathways as well as all of the similarities.
| Follow the links on the enzyme name to learn more about its chemistry and its catalytic mechanism. There are also some rationales about how the pathways fit together, which reactions are the same and which must be different to maintain favorable standard free energies for both overall pathways |
| Glycolysis |
. |
Gluconeogenesis |
. |

Glucose |
. |
ATP ->
Hexokinase
ADP <- |
 |
-> Pi
Glucose-6-Phosphatase |
| . |
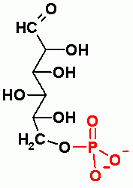
Glucose-6-Phosphate |
. |
| Phosphoglucose Isomerase |
 |
. |
| . |
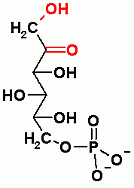
Fructose-6-Phosphate |
. |
ATP ->
Phosphofructokinase
ADP <- |
 |
-> Pi
Fructose-1,6-Bisphosphatase |
| . |

Fructose-1,6-Bisphophate |
. |
| Fructose 1,6 bisphosphate aldolase |
 |
. |
| Trisose Phosphate Isomerase |
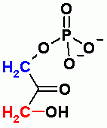
DiHydroxyAcetone Phosphate
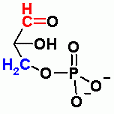
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
|
. |
NAD+ + Pi ->
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase
NADH <-
|
 |
. |
| . |
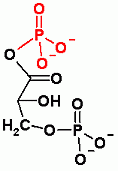
1,3BisphosphoGlycerate |
. |
ADP ->
Phosphoglycerate Kinase
ATP <- |
 |
. |
| . |
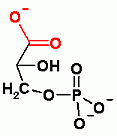
3 PhosphoGlycerate |
. |
| Phosphoglycerate Mutase |
 |
. |
| . |
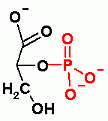
2-PhosphoGlycerate |
. |
| enolase |
 |
. |
| . . |
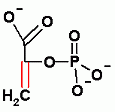
PhosphoEnolPyruvate |
. |
| .. |
. |
. |
 |
-> CO2 + GDP (ADP equivalent)
PEP carboxykinase
GTP (ATP equivalent) |
| Compare the glycolysis, uncatalyzed and gluconeogenesis reactions side by side |
ADP ->
Pyruvate Kinase
ATP <- |
 |
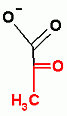
oxaloacetate
4 Carbon compound |
|
| . |
. |
. |
 |
-> ADP + Pi
pyruvate carboxylase
<- CO2 + ATP |
| . |
 |
. |
| ---glycolysis "officially" ends here, but 1 of the 3 step below are required!-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
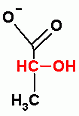
pyruvate decarboxylase
Ethanol fermentation: Beers, Wines The CO2 released is used to raise bread |
 |
. |
 |
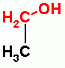
lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate fermentation:(overworked muscle cells, red blood cells, yogurt making (Lactobacillus acidophilus)) |
| . |
 |
 |
 |
. |
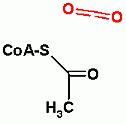
pyruvate dehydrogenase
This is NOT used in fermentative processes! This takes place in mitochondria and MUST lead to oxidative glucose metabolism. |
 |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |






















