|
Glycolysis PEP is converted to pyruvate along with production of an ATP.
|
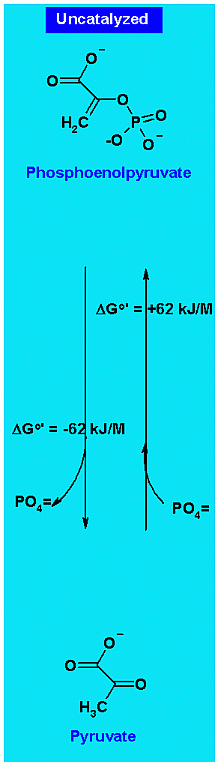
Uncatalyzed Hydrolysis of the phosphate from PEP is shown and then the addition of phosphate to pyruvate.
As these are direct reverse reactions notice that the magnitude of the ΔGo' are the same but that the signs are opposite.
|
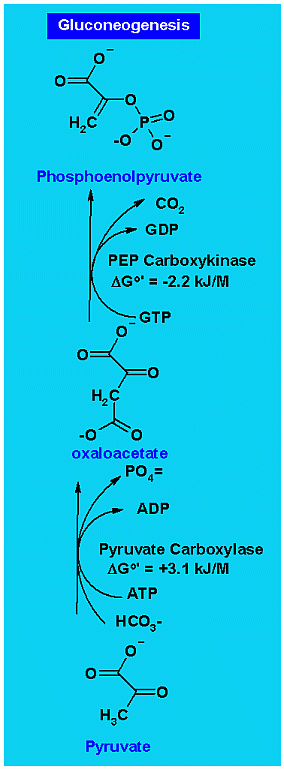
Gluconeogenesis there are two steps in getting from Pyruvate to PEP in gluconeogenesis each using an ATP equivalent (one acutualy uses GTP but it the the "TP" that matters here.) Notice that the SUM of the ΔGo' of the two reactions is about zero (+0.9). As two ATP equivalents are used to do the entire process and EACH ATP equivalent is about -31 kJ/M, the total energy change in gluconeogenesis reactions is about right.
|