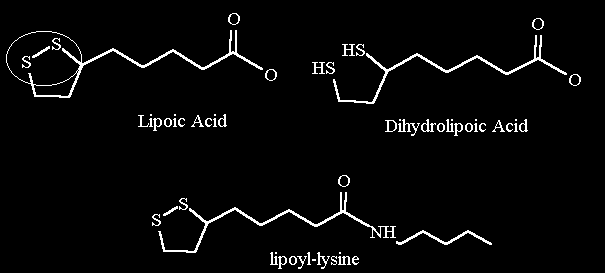
In its oxidized (top left) and reduced (top right) states.
It is always covalently attached to an enzyme via an amide bond to a Lysine.

 |
|
| Chemical structure lipoic acid and lysyl-lipoamide. In its oxidized (top left) and reduced (top right) states. It is always covalently attached to an enzyme via an amide bond to a Lysine. |
3D structure of reduced lipoic acid. It is shown covalently linked to the enzymes Lysine (to the left side of the structure) |
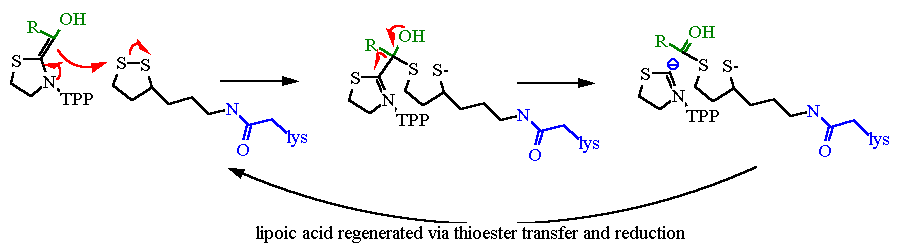
| Lipoic acid is involved in enzymes that catalyze the oxidative decarboxylation of an α-keto acid. Its function is to provide "transport" from the decarboxylation active site to the "oxidation" active site within the enzyme. It is used mostly in conjunction with Thiamine Pyrophosphate as shown below. | |
 | |