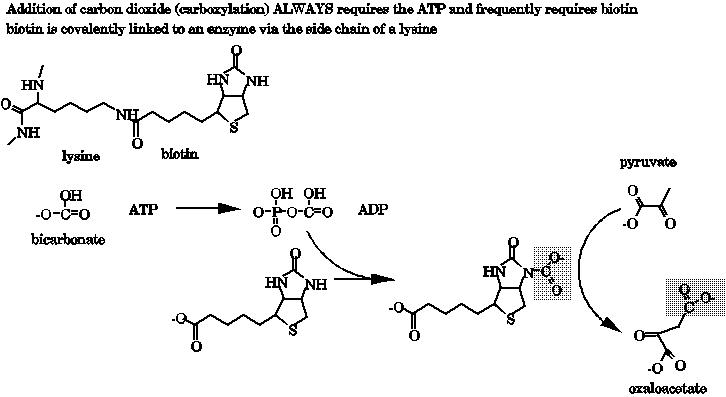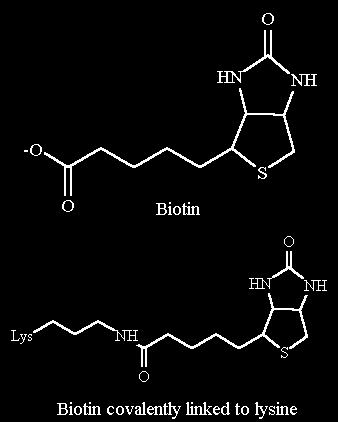
Biotin is a cofactor that is involved with carboxylation reactions. (an organic acid is added to a compound using CO2 in the form of bicarbonate). In a carboxylation reaction ATP must be hydrolyzed to activate the CO2 as shown below. Then a carboxybiotin intermediate is formed that is the carboxylating agent. The CO2 is added in an Aldol Reaction most frequently requiring a metal ion to drive the formation of the transition state.
 HCO3- + H+
HCO3- + H+