|
Enzyme Name |
Phosphoglucose Isomerase | |
Reaction Catalyzed |
Isomerization of Glucose-6-P to Fructose-6-P  | |
Reaction Type |
Isomerization | Pathway Involvement |
Both Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis |
This reaction is freely reversible and in fact the STANDARD Free Energy of this reaction favors gluconeogenesis by a little bit. The observed reaction direction can easily be influenced by the substrate and product ratio (ΔG for these conditions - check out the thermodynamics tab) |
Cofactors/Cosubstrates |
None | |

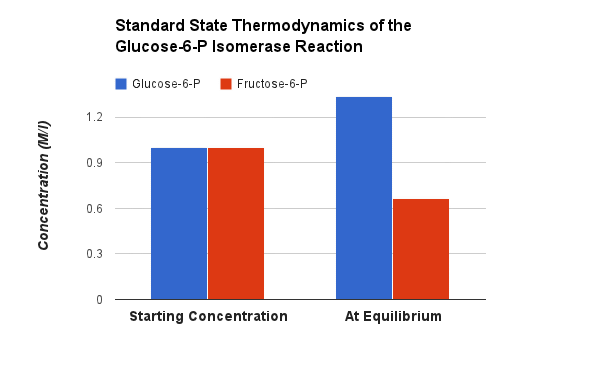
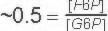
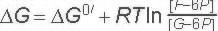
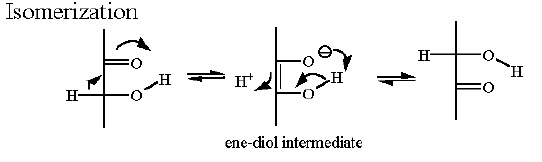
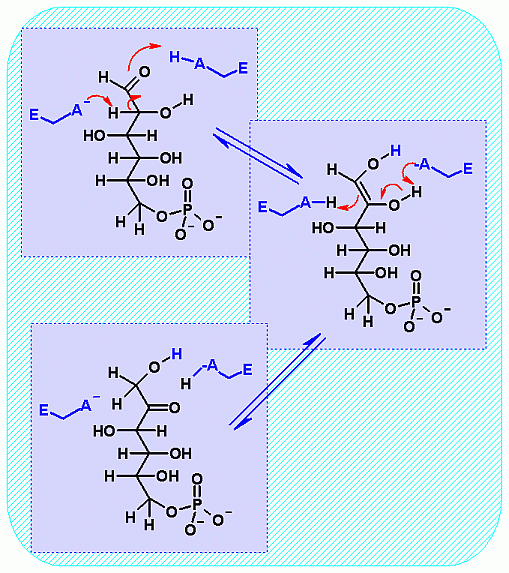
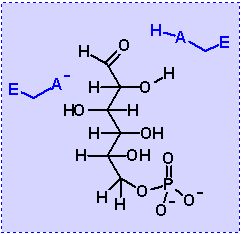 Phosphoglucose Isomerase. Animation of an Phosphoglucose Isomerase reaction Blue: represents the enzyme. The EA- and EAH represent the crucial enzyme active site amino acids in their basic (deprotonated) and acid (protonated) states, respectively. "Start" begins an animation of the isomerization reaction. It proceeds through the reaction in the "forward" direction and then "backwards" again. Note how the enzyme is involved. "+" increases speed while "-" decreases the animation speed. You may also step through the reaction using "next" or "previous"
Phosphoglucose Isomerase. Animation of an Phosphoglucose Isomerase reaction Blue: represents the enzyme. The EA- and EAH represent the crucial enzyme active site amino acids in their basic (deprotonated) and acid (protonated) states, respectively. "Start" begins an animation of the isomerization reaction. It proceeds through the reaction in the "forward" direction and then "backwards" again. Note how the enzyme is involved. "+" increases speed while "-" decreases the animation speed. You may also step through the reaction using "next" or "previous"
