|
Rationale
|
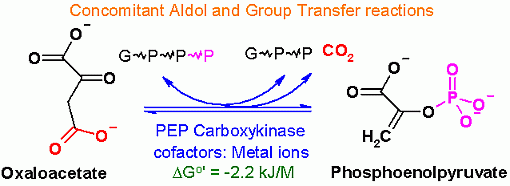
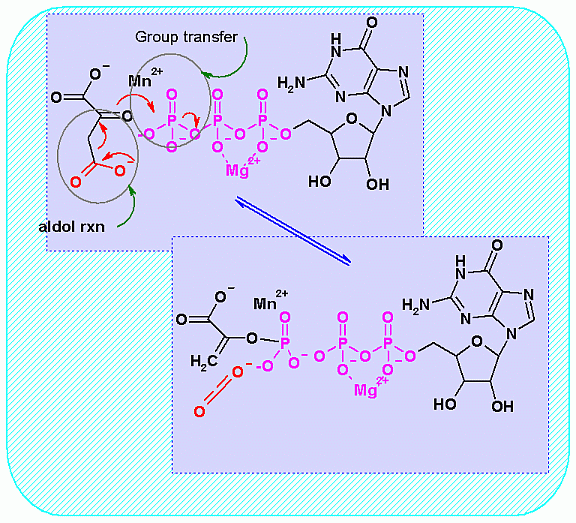
This is the second half of the two reactions that are required to bypass the pyruvate kinase reaction of glycolysis. This one takes the smae carboxyl group that was just put onto pyruvate by the pyruvate carbolylase enzyme. This uses the Free Energy of generating a CO2 from and Aldol cleavage to drive the "enol" formation and then the the "enol" attacks GTP for a group transfer reaction.
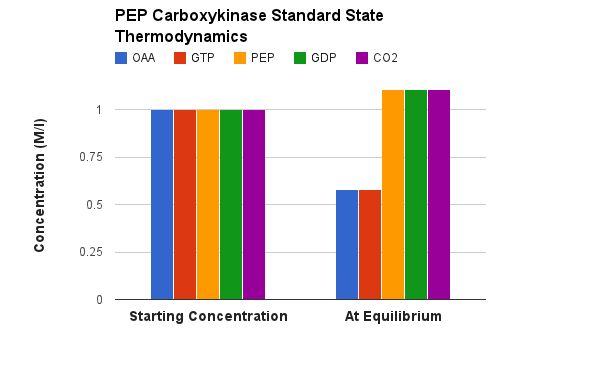
while the ΔGo' is not very far from 0, this reaction is virtually irreversible in reality toward product phosphoenolpyruvate. The reason is that CO2 concentrations are very low in the tissues. We go to great lengths to keep our CO2 concentration low. There are two mechanisms:
- In the tissues, where CO2 is generated and therefore in relatively high concentration, an enzyme called Carbonic Anhydrase (CA) rapdidly converts CO2 to HCO3- + H+ by reaction with water in a reversible reaction.
- In the lungs, where CO2 concentration is low (atmosphereic concetrations), the same reaction catalyzed by the same enzyme runs the other way to generate CO2 so that we can exhale it.
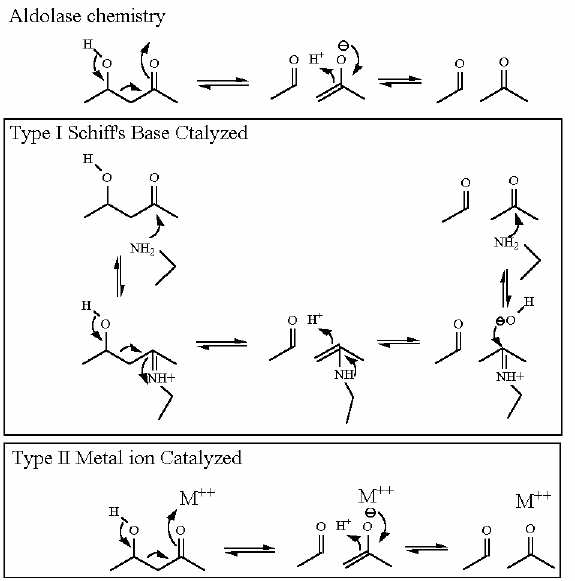
A metal ion helps the aldol reaction get started by providing a strong positive charge to start the electron pulling.
|