This is the dominant form
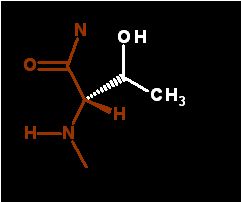
There is very little of this under normal conditions
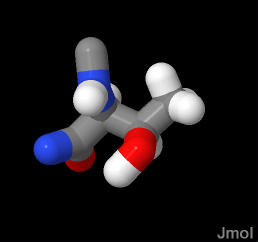

Polar amino acid can act as a hydrogen bond donor or acceptor. This is Threonine's most frequent role in structure. The pK of about 15 for the sidechain -OH is way above the physiological range. Normally deprotonation of this group can be ignored.
Like Isoleucine there is a branch atom on the β-Carbon. Just as in isoleucine this restricts some of the conformations allowed relatice to other amino acids.
In the demonstration below, the threonne is in a section of random coil and is exposed to water on the surface of the protein.
|
Click an atom to diplay it's identity here | |
|
Messages about the currently highlighted features |