
 |
|
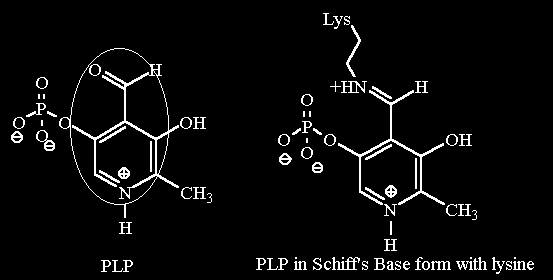
| Chemical structure pyrodoxal phosphate and its Schiff's Base conjugate with lysine | 3D representation of PLP |
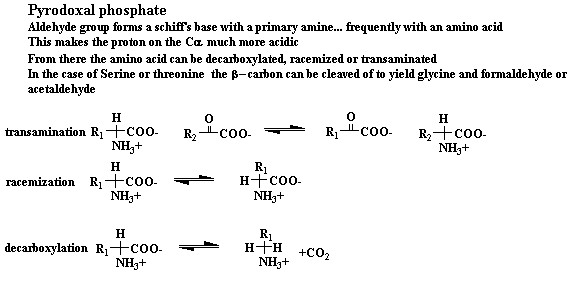
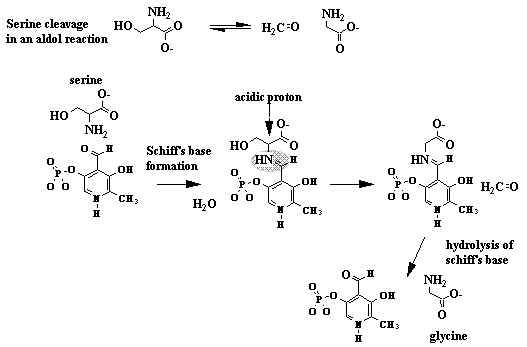
| PLP is involved in many different type of reactions (see below). Generally it forms a Schiff's Base with the amine group of amino acid. It can then perform a transamination of amino acids, or a decarboxylation or a racemization of the α Carbon or even a dehydration of a serine residue. | |
  | |