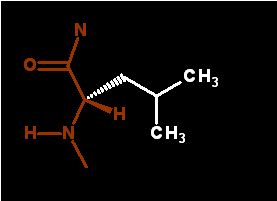
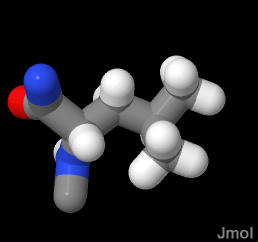

Hydrophobic, not likely to be found in a turn. Very unlikely to be exposed to water.
The "Leucine Zipper" motif can be found at the interface subunits in some dimeric proteins. Leucines from opposing subunits can interdigitate via the hydrophobc interaction and literaly "zip up" to form a very stable interaction.
In the demonstration below, the Leucine is part of a β-sheet and is buried deep in the protein structure well secluded from water
  Atom Label Description | |
|
Click an atom to diplay it's identity here | |
|
Messages about the currently highlighted features |