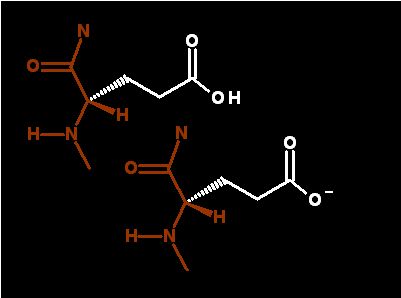
dominant form at physiological pH
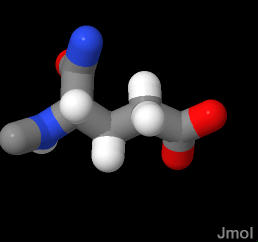

glutamic acid (Glutamate) ends in an organic acid which ionizable (can lose a proton to solvent and becomes negatively charged)
At physiological pH of 7 the the terminal acid in glutamate is generally unprotonated (in the base form and negatively charged) it is frequently exposed to water as it is in the demonstration below. In this case, the glutamate is found in β-sheet. The negatively charged organic acid is in contact with the end of another amino acid sidechain - the postively charged amine group of lysine 85. See if you can identify this in the last step of the demo.
  Atom Label Description | |
|
Click an atom to diplay it's identity here | |
|
Messages about the currently highlighted features |