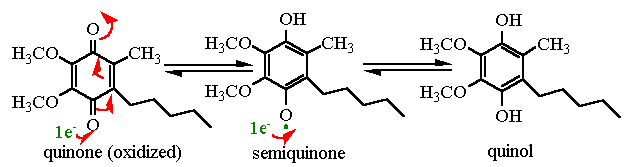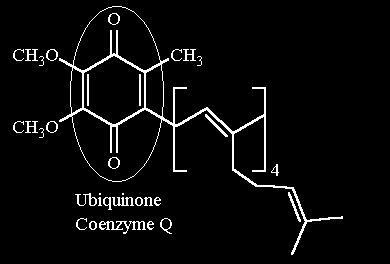
Coenzyme Q (ubiquinone) is part of the electron transport pathway of oxidative phosphorylation as well as that of photosynthesis. It is a membrane soluble cofactor that can take up 1 or 2 electrons as well as an appropriate number of protons. In the oxidative phophorylation pathway it is the electron tranporter immediately following "complex I" or "complex II"
You can buy a version of this at the grocery store - usually labeled as "Q10". It is sold as an aid for converting energy more efficiently. It's not a vitamin in the classic sense - we do synthesize it. A reasonable diet shoud also provide suffieient amounts as well. There are, of course, cases where genetic defects in the enzymes required for synthesis CoQ require an external supplementary source.