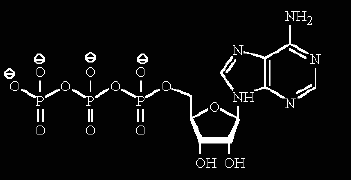
ATP provides one of the main energy storage mechanisms in cells. The standard free energy (ΔGo') of hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases about 31 kJ/mol of energy. The energy released is used: to drive unfavorable chemical reactions, allow mechanical motion, phosphorylation of substrates and enzymes or other energy requiring factors.
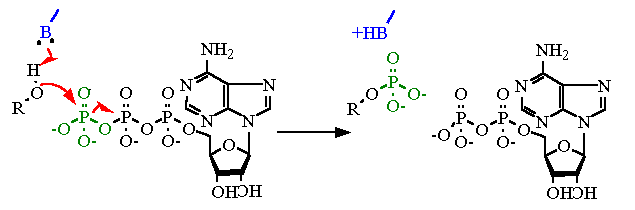
As shown in the reaction below it is an hydrolysis reaction which means that it is -for all practical purposes - irreversible EXCEPT under special circumstances.
These special cirumstances include:
- Group transfer from another high energy phosphate compound (1,3 bisphosphoglycerate) - more on this in the metabolism section.
- The input of mechanical energy driven by the H+ gradient from complex V (ATP synthase in the oxidative phosphorylation system discussed in module 8)
- hexokinase
- F1 ATPase
- pyruvate carboxylase
- Others too many to enumerate
