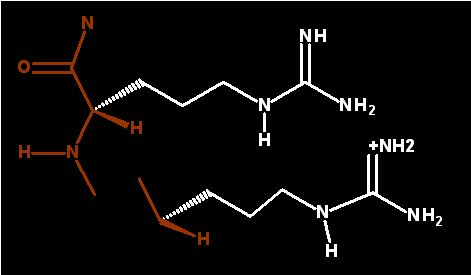
Protonated (acid form - positively charged)
Dominant form at physiological pH
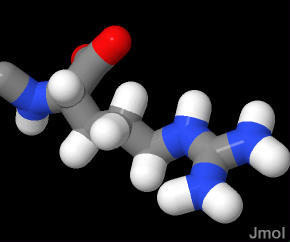

The group at the end of the sidechain includes three N and 1 C is termed a "Guanidinium" group. With a pK of 12 this group is almost always in the protonated and ionized state. Notice how planar the goup is.
In the demonstration below the Arginine is the last amino acid (106) in the protein shown. The charge on the sidechain means that is will frequently be exposed to water as it is in this demonstration.
  Atom Label Description | |
|
Click an atom to diplay it's identity here | |
|
Messages about the currently highlighted features |