 Glycerate Mutase Information
Glycerate Mutase Information Glycerate Mutase Information
Glycerate Mutase Information
|
Enzyme Name |
Glycerate Mutase
|
|
|
|
||
|
Reaction Catalyzed |
Group Transfer of phosphate from C3
to C2 of glycerate
|
|
|
Reaction Type |
Group Transfer Reaction |
|
|
Rationale |
This is a group transfer reaction. This is most easy to
visualize when you look at the mechanism of the reaction (see below).
The phosphate is transferred from one alcohol to another through a
phopshoenzyme intermediate. In effect there are two group transfer
reaction... 1. transfer of phosphate to the enzyme and 2. transfer of
phosphate from the enzyme back to glycerate. Why is Phosphate moved from C3 to C2 -
what good is it? This is justified by the next two reactions. Recall
what I said about glycerate kinase - that we can transfer a PO4
to ADP by group transfer if the Standard Free Energy favors it (or is
at least close). Right now we are trying to build to one those
compounds that has a very high Standard Free Energy of hydolysis for
the phosphate group. That high favorable Free Energy will be used to
geneate another pair of ATP. |
|
|
Pathway Involvement |
Glycolysis AND gluconeogenesis |
|
|
Cofactors/Cosubstrates |
Many required an active site metal ion to alter the ionization of the important alcohol groups (see mechanism below). |
|
|
|
||
|
DGo' |
+4.4 kJ/M |
Starting from standard state and allowing the reaction to come to equilibrium the 3-phosphoglycerate concentration would end up ~6 times higher than that of 2-phosphoglycerate. The Standard Free Energy favors Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate production. |
|
Keq |
 |
|
|
Comments |
This enzyme proceeds through a mandatory
phospho-enzyme intermediate (phsophate is covalently linked to an amino
acid side chain of the enyzme). The phospho-enzyme intermendiate then
transfers the phosphate back to glycerate. |
|
|
"In cell" Substrate Concentrations* |
||
|
S1 = |
3-Phosphoglycerate | 0.12 mM |
|
S2 = |
|
|
|
P1 = |
2-Phosphoglycerate |
0.03 mM |
|
P2 = |
|
|
|
DG for these conditions |
 |
|
|
+0.9 kJ/M ... thus under cellular conditions the reaction favors foramtion of 3 phosphoglycerate by a little bit |
||
|
|
||
|
Mechanism for Chemistry |
 |
|
|
Mechanism for Enzyme |
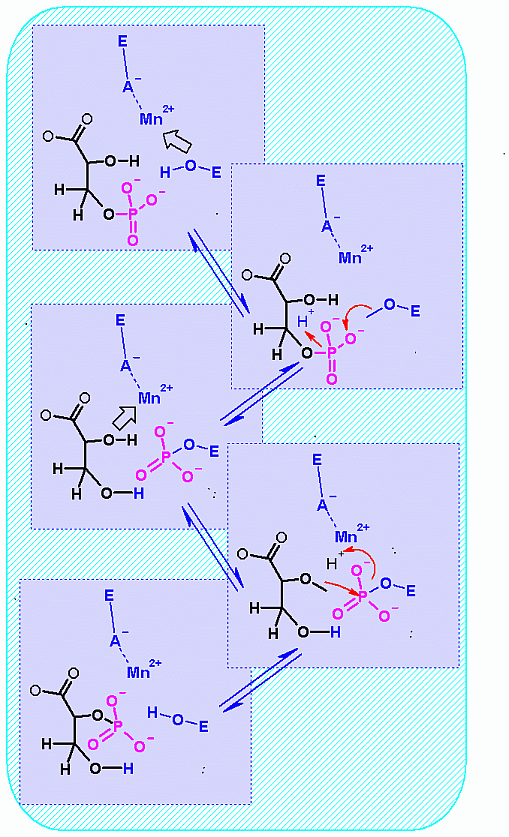
|
|
|
Picture of Enzyme with substrate |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Click on an atom to diplay identity here | |
|
|