Enzyme Name
Glycerate Kinase
Reaction Catalyzed
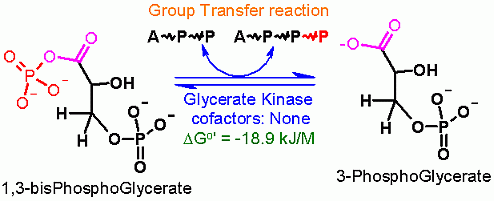
Group Transfer from 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate to ADP to make ATP
Reaction Type
Rationale
A group transfer of phosphate onto ADP to make ATP is made thermodynamically favorable even starting from the standard state because the phosphate is coming off of an organic acid. Please recall a couple modules ago, a quiz question dealt with the Free Energies of a phosphate hydrolysis from two different functional groups: 1. an alcohol, 2. an organic acid; the Standard Free Energies differed substantially at -17 kJ/M and -42 kJ/M respectively. This will be described in more detail in later pages of this module, but the energy of hydrolysis can be linked to another reaction (in this case the transfer of a phosphate onto ADP to make ATP). In terms of thermodynamics, these two reactions can be considered as individual half reactions and can be combined into a single overall reaction such that the favorable Free Energy of one "half reaction" can be used to counteract the unfavorable Free Energy of another. In this case
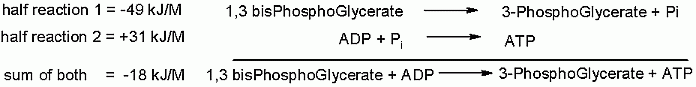
Pathway Involvement
Glycolysis AND gluconeogenesis
Cofactors/Cosubstrates
ADP is a cosubstrate in glycolysis direction and ATP is a coproduct
ΔGo'
-18.9 kJ/M
Starting from standard state and allowing the reaction to come to equilibrium the 3-Phosphoglycerate and ATP concentration would end up ~200 times higher than the product of the concetrations of 1,3bisPhosphoglycerrate and ADP.
The Standard Free Energy favors ATP production - the reason for this is outlined above.
Keq
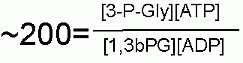
Comments
For each glucose that started glycolysis there are two glycerates. so 2 ATP are made for each of these reactions.
Our total ATP for glycolysis is now even. It took two ATP to get the pathway started (1 for hexokinase, 1 for phosphofructokinase-1). Now those two ATP have been returned. In terms of what the organism needs most.. energy transfer from sugar to ATP we are now even.
"In cell" Substrate Concentrations*
S1 =
S2 =
P1 =
P2 =
ATP
1.85 mM
ΔG for these conditions
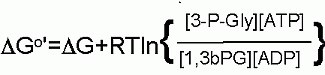
+0.1 kJ/M
Mechanism for Chemistry
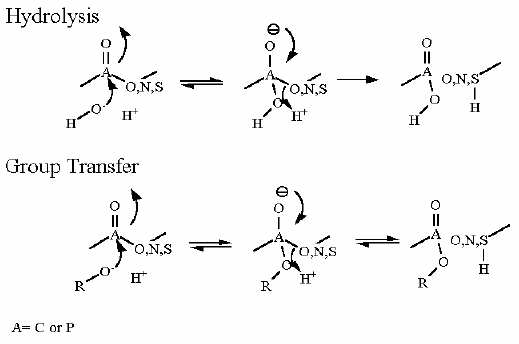
Mechanism for Enzyme

Picture of Enzyme with substrate
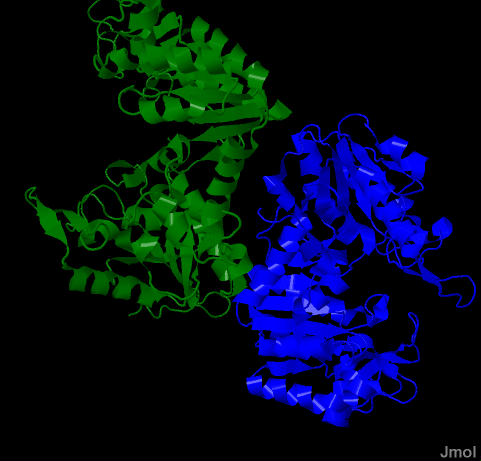
- Ribbons 3-P Glycerate. Initial picture displayed; All of the main chain of the enzyme are displayed as ribbons. There are two identical subunits.
- One subunit with 3P-Glycerate The (Glycolysis) Product 3-PhosphoGlycerate is represented as atom colored spheres C=Gray, P=Orange, O=Red. There is one each in the active sites of each subunit. Only one is displayed for clarity.
- as above includes ADP The (Glycolysis) Substrate ADP as well as magnesium (light green) is added to the active site - NOTE: one molecule is a substrate and the other a product. There is a pretty big space between them. There is a 'missing' Phosphate in this picure - This psace is where that phosphate would be
- Active Site Amino Acids AddedThe active site amino acid side chains around the 3-PhosphoGlycerate and ADP are added as the sticks - NOTE: the extremely high density of positively charges AA (LYS, ARG, HIS) around the Glycerate
- Prteon Ribbons removed The Ribbons representing the protein backbone is removed from the picture.
- Reactive groups highlighted The Caryboxyl group of 3P Glycerate and the terminal O-P atoms of ADP are colored cyan - Note their proximity. the extra space would be filled with a Phosphate gropup in the real reaction.
