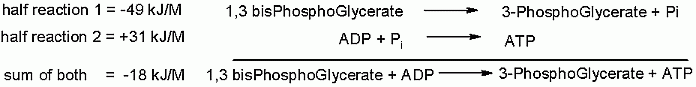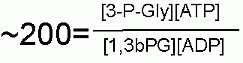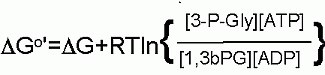|
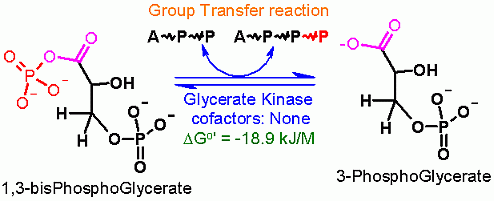
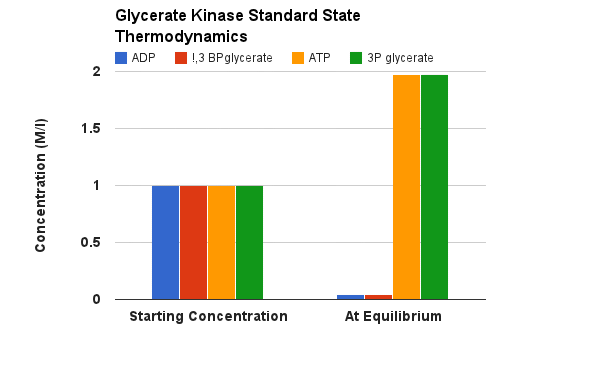
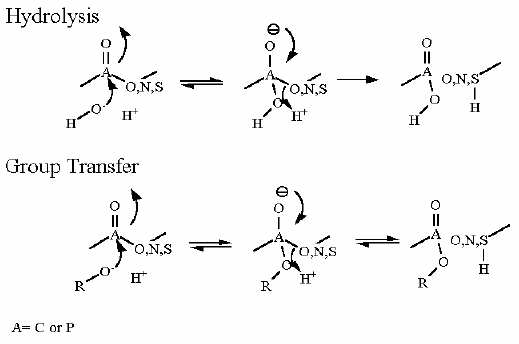
A group transfer of phosphate onto ADP to make ATP is made thermodynamically favorable even starting from the standard state because the phosphate is coming off of an organic acid. Please recall a couple modules ago, a quiz question dealt with the Free Energies of a phosphate hydrolysis from two different functional groups: 1. an alcohol, 2. an organic acid; the Standard Free Energies differed substantially at -17 kJ/M and -42 kJ/M respectively. This will be described in more detail in later pages of this module, but the energy of hydrolysis can be linked to another reaction (in this case the transfer of a phosphate onto ADP to make ATP). In terms of thermodynamics, these two reactions can be considered as individual half reactions and can be combined into a single overall reaction such that the favorable Free Energy of one "half reaction" can be used to counteract the unfavorable Free Energy of another. In this case
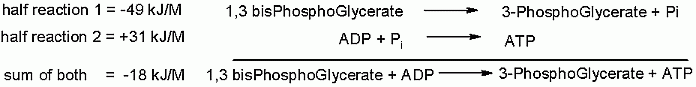
For each glucose that started glycolysis there are two glycerates. so 2 ATP are made for each of these reactions.
Our total ATP for glycolysis is now even. It took two ATP to get the pathway started (1 for hexokinase, 1 for phosphofructokinase-1). Now those two ATP have been returned. In terms of what the organism needs most.. energy transfer from sugar to ATP we are now even.
|