|
Enzyme Name |
Glucose-6-Phosphatase |
||
|
Reaction Catalyzed |
Hydrolysis of phosphate from Glucose-6-Phosphate
|
||
|
Reaction Type |
Hydrolysis |
||
|
Pathway involvement |
Gluconeogenesis ONLY |
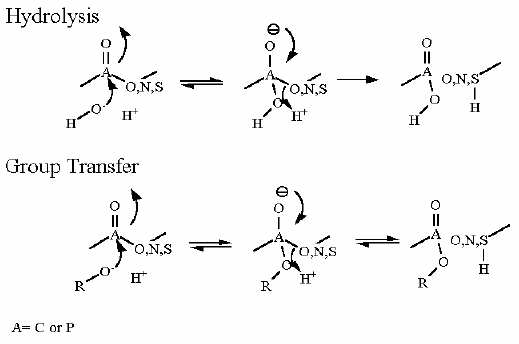
Glucose-6-Phosphatase is not part of the glycolysis pathway. In glycolysis a separate enzyme (Hexokinase) adds a phosphate onto Glucose and is ATP dependent. The reaction catalyzed by Glucose-6-Phosphatase is a hydrolysis which in water is extremely difficult to reverse- because water is in very high concentration. |
|
|
Cofactors/Cosubstrates |
None |
||

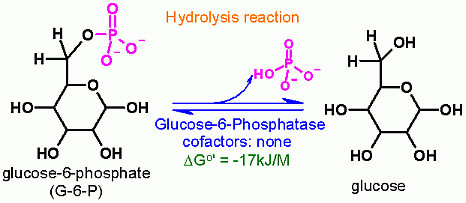
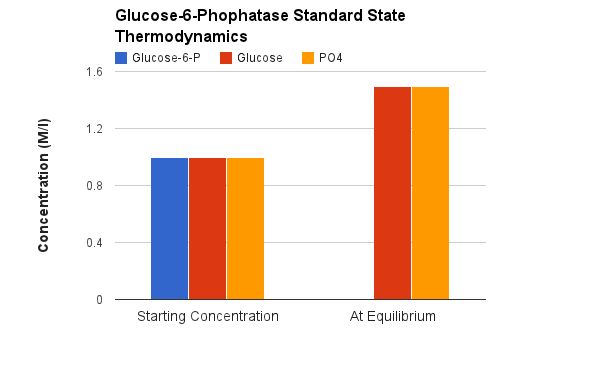
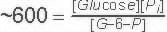
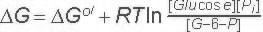
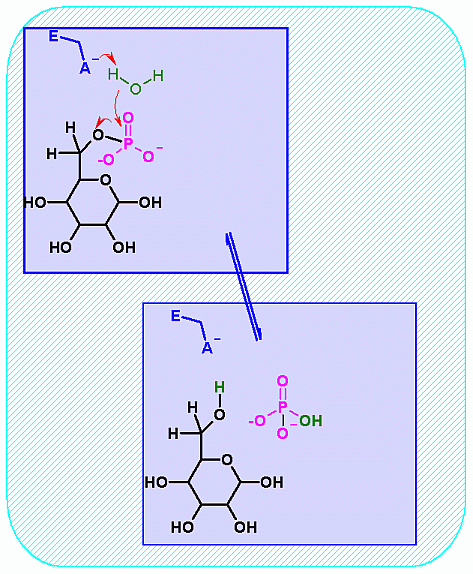
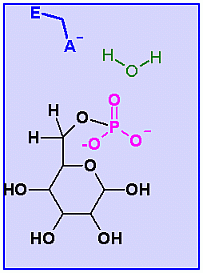 Glucose-6-Phosphatase. Animation of a Glucose-6-Phosphatase reaction Blue: represents the enzyme. THe EA- is the Aspartate from the enzyme active site in it's basic (deprotonated) state. "Start" begins an animation of the hydrolysis reaction. It proceeds through the reaction in the "forward" direction and then "backwards" again. Note how the enzyme is involved. "+" increases spped while "-" decreases the animation speed. You may also step through the reaction using "next" or "previous"
Glucose-6-Phosphatase. Animation of a Glucose-6-Phosphatase reaction Blue: represents the enzyme. THe EA- is the Aspartate from the enzyme active site in it's basic (deprotonated) state. "Start" begins an animation of the hydrolysis reaction. It proceeds through the reaction in the "forward" direction and then "backwards" again. Note how the enzyme is involved. "+" increases spped while "-" decreases the animation speed. You may also step through the reaction using "next" or "previous"