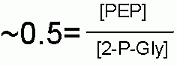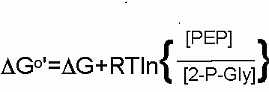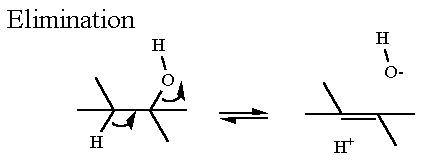|
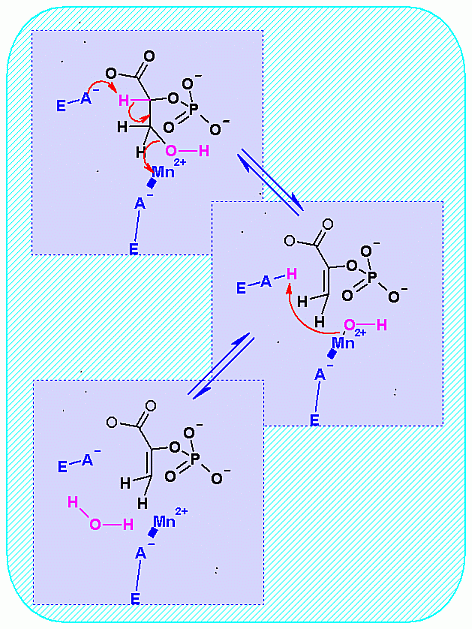
Elmination Reaction. The phosphate has already been placed on C2 of glycerate from the previous enzyme.
The Enol functional group.
Now an elimination reaction will remove a water (hydroxyl -OH group for C3aand a hydrogen from C2) The result is a double bond between C2 and C3. Compounds that contain a carbon - carbon double bonds (C=C) are always named with an ending of -ene. For example Propane is a three carbon compound with only single bonds between carbons and all other bonds are filled by hydrogen. Propene is the same except that it contains one C=C. In the case of phosphoenolpyruvate, C2 has this double bond to C3 AND it also has a hydroxy group on it as well. Therefore C2 is now named an "enol" ("en" = ene for the C=C and "ol" is for alcohol).
The significance of the Enol group
Enols are not very stable in water. Generally there is a rapid, facile, nonezymatic conversion between an enol and a ketone.This type of conversion is called tautomerization and occurs extremely quickly. Thermodynamically, the ketone form is greatly favored - therefore the ketone is in much high concentration than the enol fom.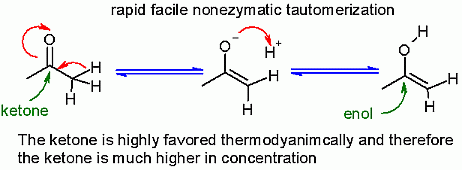
The conversion is allowed to occur only IF the the enol has an -OH on it like compound "A" ...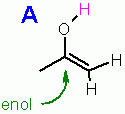 because the terminal -H must be able to dissociate as H+ for the conversion. because the terminal -H must be able to dissociate as H+ for the conversion.
In phosphoENOLpyruvate the enol does not terminate with -H but with -PO3 like compound "B"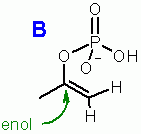 which cannot dissociate therefore the molecule is trapped in this less favorable enol form. which cannot dissociate therefore the molecule is trapped in this less favorable enol form.
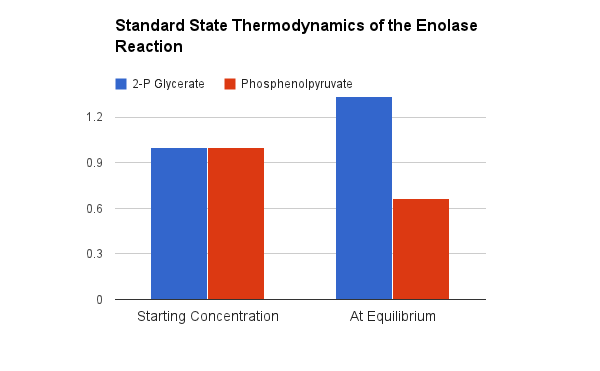
Thermodynamically speaking hydrolysis of phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate has a very high favorable Standard Free Energy because two things happen... we get the hydrolysis AND then the enol converts mostly to the much more stable ketone.
|



 because the terminal -H must be able to dissociate as H+ for the conversion.
because the terminal -H must be able to dissociate as H+ for the conversion. which cannot dissociate therefore the molecule is trapped in this less favorable enol form.
which cannot dissociate therefore the molecule is trapped in this less favorable enol form.