Formally, this reaction is simply the "removal" of water from a molecule to leave an unsaturated C as a product. The molecule must contain an alcohol group and a C-H bond on the adjacent carbon. This reaction is readily reversible both thermodynamically and kinetically. It is a little different than the previous reactions in that it does not start with a ketone. This one starts by apparently "ripping" the -OH off the alcohol carbon.
Reactions that involves the elimination of water to form a double bond generally require the presence of a good electrophile (electron pulling device) such as a metal ion to aid in OH- leaving.
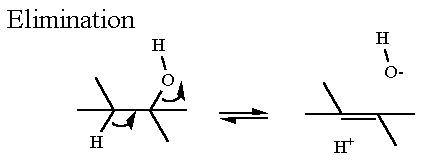
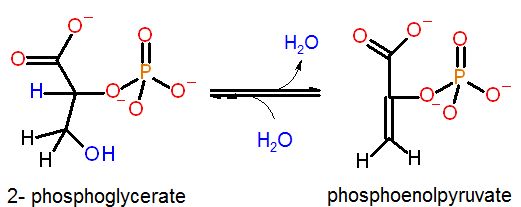 Example of elimination reaction from the glycolysis pathway. Effectively water is removed from C2 and C3 generating an unsatrauted C=C bond.
Example of elimination reaction from the glycolysis pathway. Effectively water is removed from C2 and C3 generating an unsatrauted C=C bond.