|
Enzyme Name |
Glycogen Synthase | |
Reaction Catalyzed |
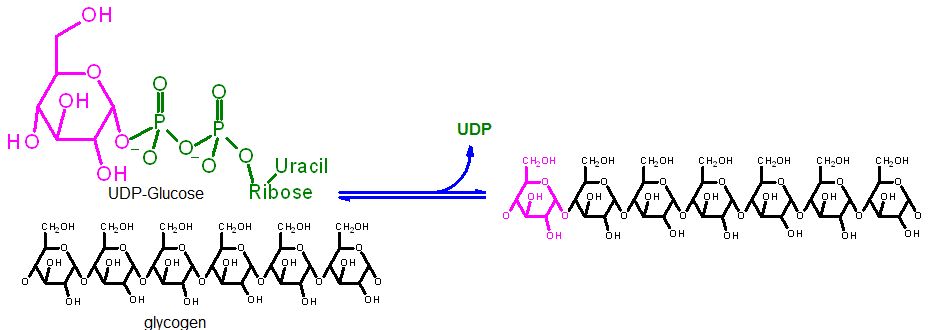
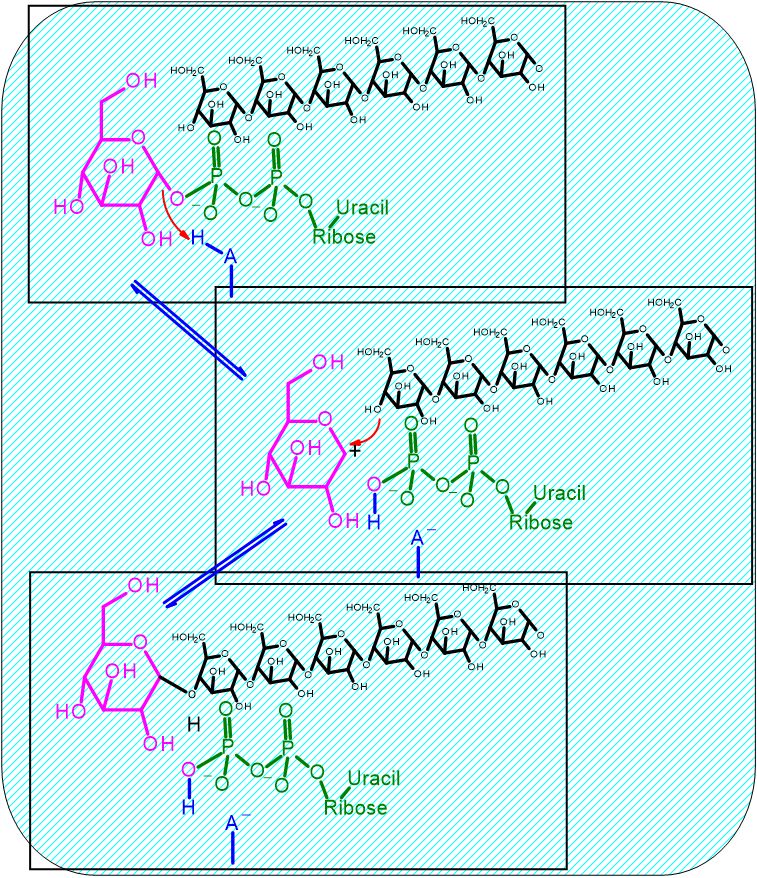
Group Transfer of glucose onto C4 (always) of the terminal glucose of the glycogen polymer
| |
Reaction Type |
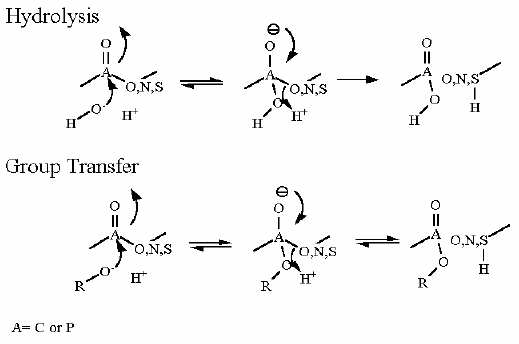
Group Transfer Reaction | |
Pathway Involvement |
Glycogen Synthesis |
|
Cofactors/Cosubstrates |
None. | |