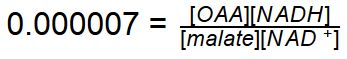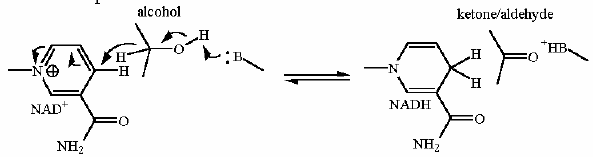|
Enzyme Name |
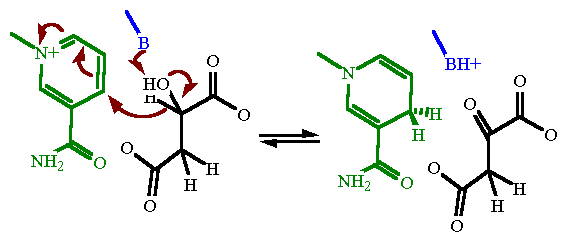
Malate Dehydrogenase |
|
| |
||
Reaction Catalyzed |
Redox
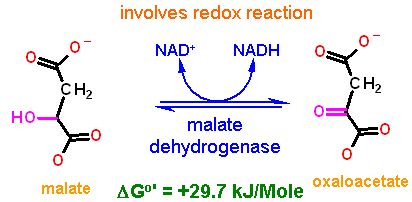
|
|
| Reaction Type |
Oxidation - Reduction
|
|
| Pathway Involvement | Citric Acid Cycle
|
|
| Cofactors/Cosubstrates | NAD+/NADH are the cosubstrate/coproduct | |